Definition Differential Heat Of Solution . Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and a solvent under constant pressure, resulting in infinite dilution. Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Heat energy = cmu, where m is the body mass, u is the. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties: Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear to any powers or in any functions.
from www.chegg.com
Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and a solvent under constant pressure, resulting in infinite dilution. Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear to any powers or in any functions. Heat energy = cmu, where m is the body mass, u is the. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties:
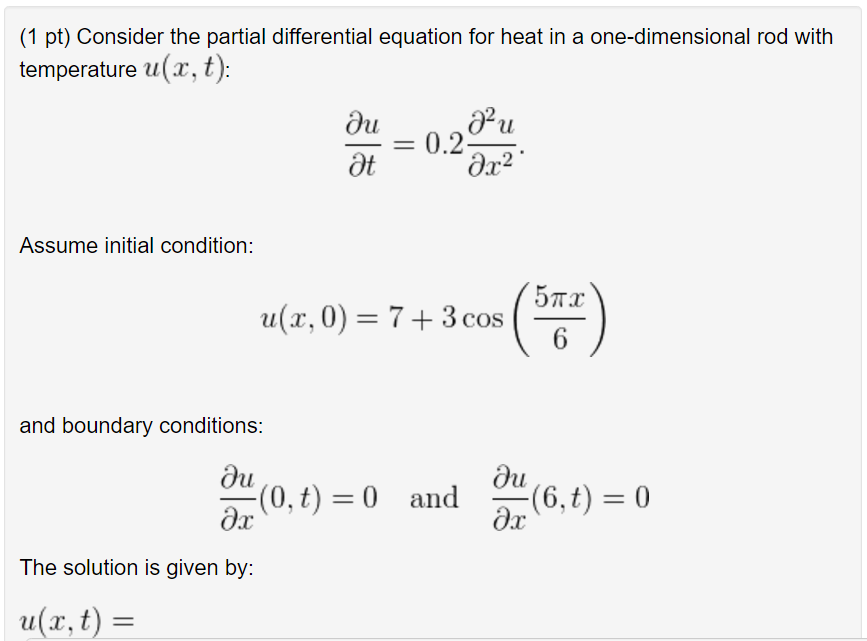
Solved Consider the partial differential equation for heat
Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear to any powers or in any functions. Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and a solvent under constant pressure, resulting in infinite dilution. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Heat energy = cmu, where m is the body mass, u is the. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties:
From chempedia.info
Integral and Differential Heats of Solution Big Chemical Encyclopedia Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.youtube.com
Heat Equation Solution by Separation of Variables & Fourier Series Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From odysee.com
Solving the heat equation Differential equations, chapter 3 Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties: Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. \[δh_{solution} =. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From owlcation.com
Differential Equations Owlcation Definition Differential Heat Of Solution \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties: Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and a solvent under constant pressure, resulting. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From submeso.org
Differential heating Turbulence and Local Circulations Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties: Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From sites.google.com
Calorimetry Preliminary HSC Chemistry Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and a solvent under constant pressure, resulting in infinite dilution. Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear to any powers or in any functions. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Formulate a solution for the heat equation shown Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear to any powers or in any functions. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.doubtnut.com
The enthalpy in the process HCl+nH2O to HCl in n moles of H2O Where n Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Heat (or thermal) energy of a body with uniform properties: Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Heat energy = cmu,. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.studocu.com
CH13 708 CHAPTER 13 Heats of Solution and Mixing 13 Heats of Solution Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From studylib.net
Differential heating Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Heat energy = cmu, where. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.researchgate.net
Differential heat curves as in Fig. 2, but including an assumed driving Definition Differential Heat Of Solution \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Heat energy = cmu, where m is the body mass, u. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The difference between heat capacity at constant Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.researchgate.net
Differential heat of reaction in 30 wt HEPZ at 313.15 K (— total Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Partial Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation ID353900 Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Heat energy = cmu, where m is the body mass, u is the. Web the heat of. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The heat diffusion equation is a parabolic partial Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed or released when one mole of the substance is. Heat energy = cmu, where m is the body mass, u is the. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.youtube.com
02 Problem of One Dimensional Heat Equation Hard problem of one Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. \[δh_{solution} = δh_1 + δh_2 + δh_3. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Web the molar heat of solution \(\left( \delta h_\text{soln} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.researchgate.net
3 Actuation principles based on a) differential heating of Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web the heat equation is linear as u and its derivatives do not appear to any powers or in any functions. Web the heat of solution is the difference in enthalpy between the dissolving solute and a solvent under constant pressure, resulting in infinite dilution. Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Consider the partial differential equation for heat Definition Differential Heat Of Solution Web therefore, since \(u(x,0)=s(x)\) for \(0\le x\le l\), \(u\) is an actual solution of equation \ref{eq:12.1.4} if and only if. Web to understand enthalpies of solution and be able to use them to calculate the heat absorbed or emitted when making solutions. Web the enthalpy of solution can expressed as the sum of enthalpy changes for each step: Web the. Definition Differential Heat Of Solution.